Muscle in Pacific
When a near-final draft of the annual National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) dropped over two weeks ago, one of the oddest things that grabbed our attention was a pilot program for contractor-operated amphibious aircraft in the Pacific. The NDAA that was subsequently passed into law had some tweaks to the language, but it was no less intriguing.
The provision reads:
EC. 381. PILOT PROGRAM FOR CONTRACTED AMPHIBIOUS AIR RESOURCES FOR THE AREA OF RESPONSIBILITY OF THE UNITED STATES INDO-PACIFIC COMMAND.
(a) AUTHORITY .—The Secretary of Defense, in conjunction with the Secretary of the Navy and the Commander of the United States Indo-Pacific Command, may carry out a pilot program for the contracted operation of a fleet of commercial amphibious aviation resources to be made available to the commanders of the combatant commands and the commanders of other components of the Department of Defense for mission tasking within the area of responsibility of the United States Indo-Pacific Command.
(b) FIELDING AND ADJUDICATING MISSION REQUESTS
The Commander of the United States Indo-Pacific Command shall establish a process to field and adjudicate mission requests pursuant to the pilot program under subsection (a) in a timely manner.
(c) TERMINATION .—The authority to carry out the pilot program under subsection (a) shall terminate on the date that is three years after the date of the enactment of this Act.
We reached out to INDOPACOM for more details about the scope and scale of this initiative almost immediately after the draft NDAA was released earlier this month, but they told us they would not comment as it was still not law. After it was passed into law, they still would not comment and as of last Friday, they sent us to the Pentagon in search of answers. We have not gotten anything back yet, but we hope to at some point. Still, this lack of information seems a bit odd for what appears outright to be a provision that is not overtly sensitive in nature and relatively straight forward.
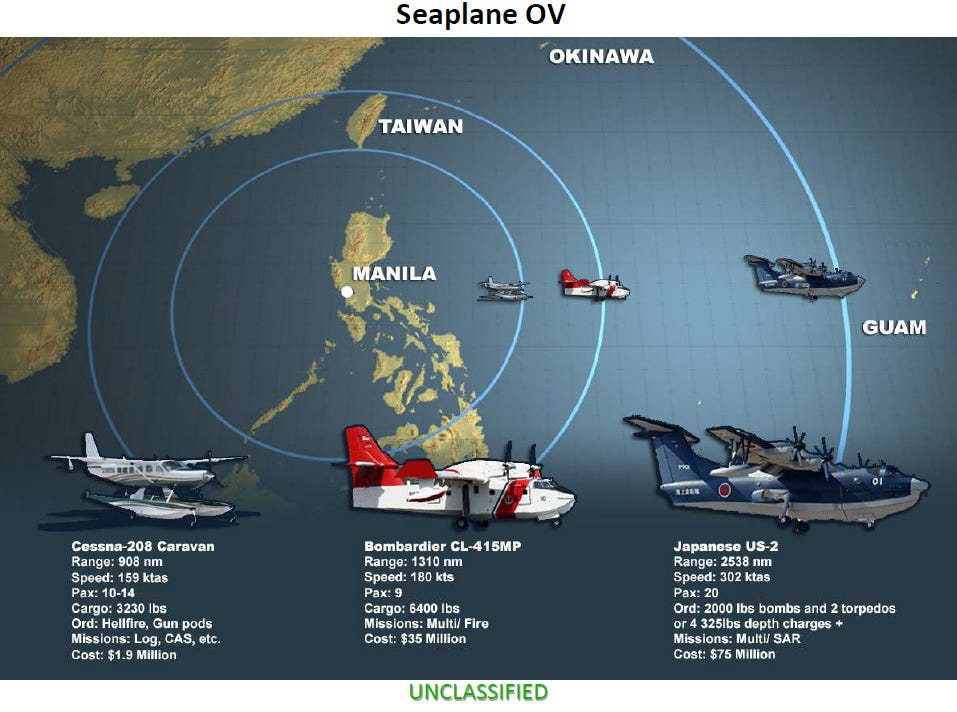
Regardless, based on the limited information we have at this time, this looks to be a program to test the use of contractor air services to fill what has become something of a glaring gap for operations in the Pacific. This has both to do with logistics and search and rescue, during peacetime and potentially (and even more pressing) during a time of war.
The lack of being able to use seaplanes to access pretty much anywhere in the vast Pacific is a missing component of the Pentagon’s growing book of capabilities to confront China. For some time, a float-equipped special operations MC-130J was seen as the Pentagon’s solution to this problem, or at least a possible solution. Eventually, after years of development and promise of near-term flight testing, that program was shuttered in 2024. Other initiatives that have looked to use waterborne flying machines to support its needs in the Pacific have also faced the axe in recent years.
Meanwhile, China is investing in advanced amphibious aircraft capabilities, and America’s tightest ally in the region, Japan, has also maintained a small fleet of highly-impressive amphibious aircraft — the ShinMaywa US-2 — for the purposes of search and rescue, with a secondary capability of accessing far flung maritime locales. Keep in mind, both of these major regional players would be fighting in their own backyard during a conflict. The United States would be mired in the most challenging expeditionary warfare it has faced in the better part of a century.
The combat search and rescue requirement is the most pressing concern when it comes to lack of amphibious flying boats or other seaplane concept. During a sustained conflict across the Pacific, aircraft will be lost, not just due to enemy action, but also due to technical failure and human error. The distances can be so far from land where this can happen that responding to such a contingency can take a long time, and that’s true even in peacetime, let alone during a time where threats will emanate thousands of miles out into the Pacific. While fixed-wing aircraft can drop additional aid to those stranded at sea, they cannot extract them. In order to do that, you need to get a ship to the survivors or get a helicopter/tiltrotor within range. The latter is already a huge problem for a major fight with China, which you can read about here. And once again, all this can take a lot of time, and that is after the crew has actually been located.
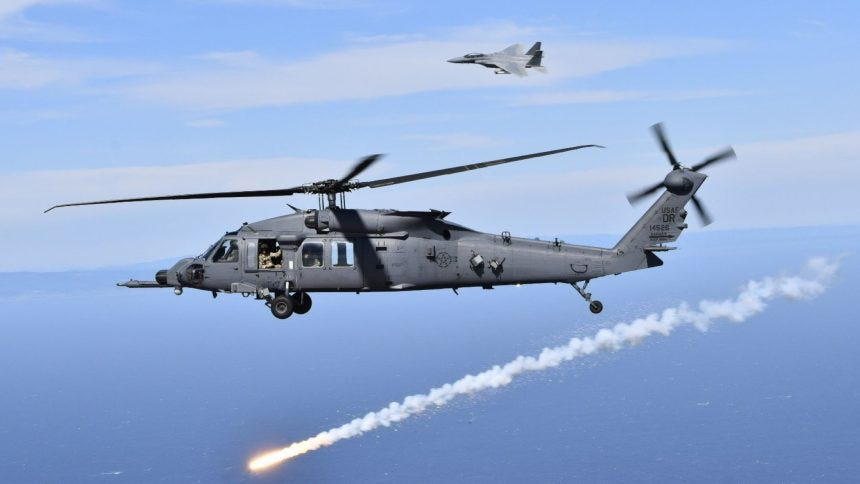

A flying boat can respond quickly and, if the sea conditons allow, it can land and recover the personnel. It can also fly low, staying under the radar horizon, for long distances. It’s in many ways an end-to-end solution, and one that can be put into action and deliver success fast when every minute counts. This was a proven capability that saved many lives during World War II when seaplanes worked to find and rescue downed aircrew and sailors. U.S. military seaplanes continued to serve in this role through the Korean War and the Vietnam War. The HU-16 Albatross amphibian aircraft also remained in U.S. Coast Guard service in the 1980s.
The other part of this, as mentioned earlier, is just providing light logistical support to very remote locales — islands in particular — that can only be accessed by certain types of aircraft. In some cases, fixed-wing aircraft can’t reach them at all. Here is where amphibians can come into play to enable small forces to operate on tiny pieces of land in the middle of nowhere, something that is firmly in the center of the Pentagon’s current Pacific strategy.
Even for airfields with runways, you don’t need a C-17 or even a C-130 to do many logical tasks. A 15-pound part, such as a component for a fighter aircraft or other system, can be the primary “need it yesterday” cargo aboard a USAF airlifter. Using smaller amphibians could free up the U.S. military’s traditional airlifter fleet for missions that demand their unique capabilities, and by all indications, they will be tasked to the absolute max during even a limited conflict in the Pacific theater. China is developing uncrewed aircraft for these kind of tasks, with many types in testing, while the U.S. lags behind.
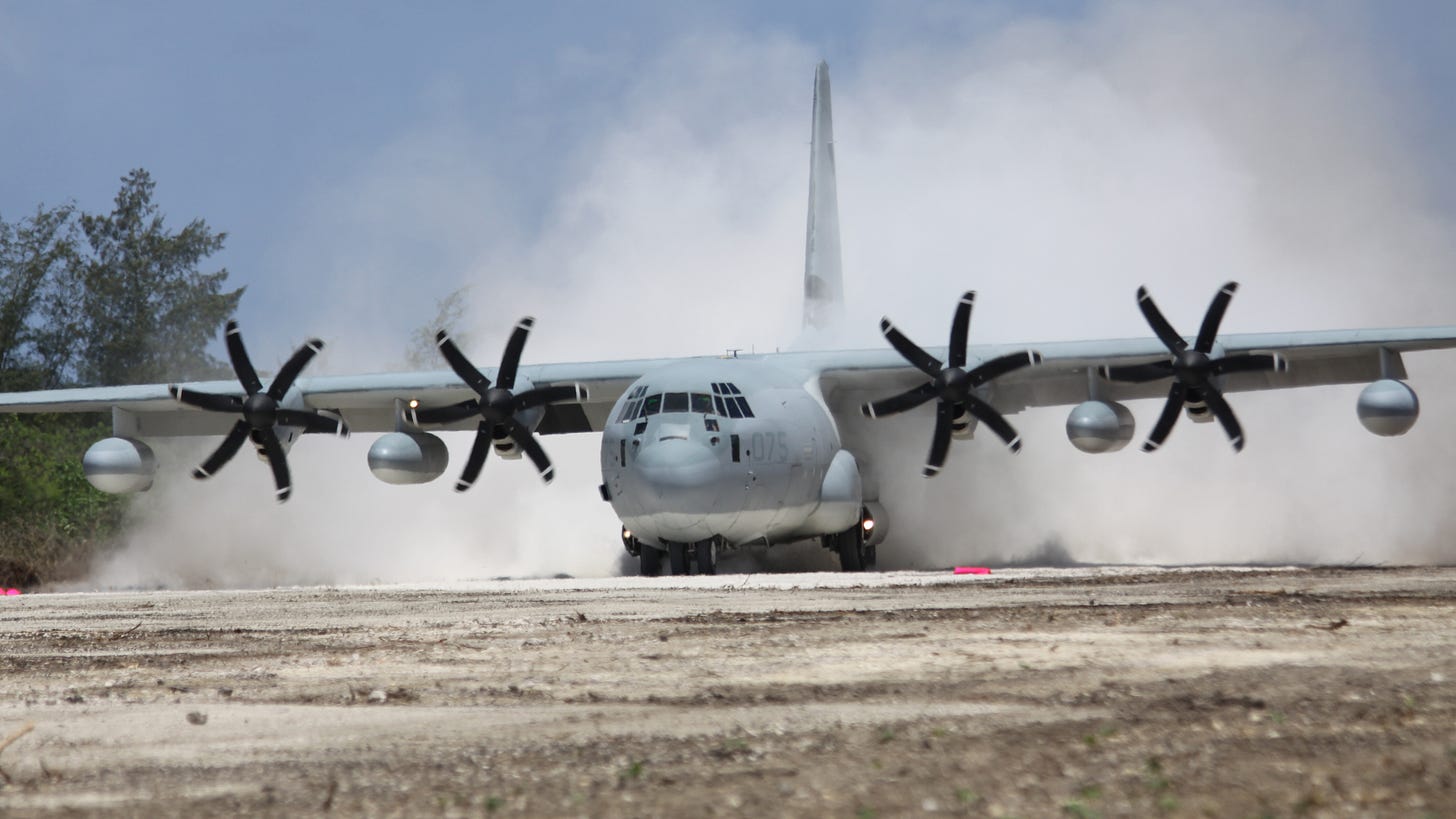

So, with all this in mind, it would seem INDOPACOM wants to experiment with the amphibian concept by using a far more elastic model than procuring aircraft and standing up a unit to fly them itself by going with the contractor model at first. Such a pilot program could reduce risk and provide some level of capability in the shorter term. At the same time, some will argue that the U.S. has no time to toy with the concept and needs its own aircraft now for a potential looming fight with China.
The CL-415 Super Scooper is a less capable, but proven solution, though it is primarily used for firefighting today. On one hand, this is a positive as contractor operators of the type already exist. On the other hand, these aircraft are in high demand for their primary role.
There is also the possibility that a floatplane could be used, such as a Cessna Caravan, but that would be far less capable and more limited in its use cases than the other two aircraft listed above.
Regardless, we will have to watch to see how this plays out, and hopefully the Pentagon will give us some clarity on the intent behind this provision. As it sits now, it looks like INDOPACOM has the chance to get some amphibious planes into action, at some point, at least to find out if they like what they see.
===========================
If you feel powerless to help Gaza, you still has a choice: donate. When so much of what exists is false, authenticity is a powerful weapon we can wield that the state never could. So if you feel lost, hopeless, depressed, angry and afraid, I implore you to return - again - again - and again - to the feeling of love that exists within you that brought you here in the first place. It is only through this that we can remake the world. To redress Gaza’s famine, displacement, and destruction, independent and impartial humanitarian organizations - UN agencies, international and national NGOs - must be allowed to deliver relief at scale. To salvage Gaza’s people from the devastation inflicted by Israel, it must be unified with the West Bank to form an independent and sovereign Palestinian State, not to be parceled and colonized by the former.
Meanwhile, children continue to be shredded by US bombs, and the starvation reaches new depths of hellish collective punishment. If both parties are going to continue to support an ongoing genocide, at least they can both be honest about doing so, rather than having one openly bloodthirsty party, and another—unconvincingly—playing the role of powerless, bumbling humanitarian.
Please keep donate Gaza especially if you, as reader, has [background] International Relation [whatever universities]. IR Graduate means [you must, at least] get some semester [about] studying Middle East [in macro, not specifically Gaza].
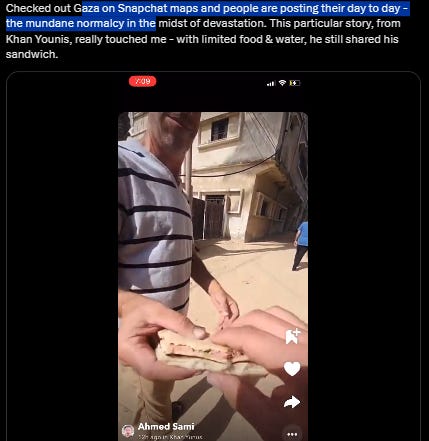
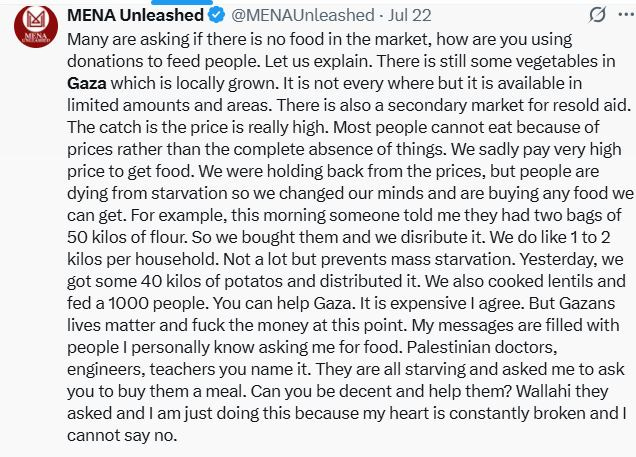
We need more people to share fundraisers instead of only talking about Gaza. Some people think that those in Gaza don’t need money but that’s wrong. Almost everyone lost their source of income while essentials, food & medicine get sold for astronomical prices. So I put my attempt in all social media as I can, in twitter / X, in substack [since October 2023 I put link donation], in bluesky or bsky, in threads, in instagram.
Link to donate World Food Programme - Palestine appeal: click here
[Daniel Brühl]
Most campaign shared or circulated in social media are for REAL people in Gaza. They’re legit. There are a lot of small campaigns for struggling families. This is their only lifeline. By donating & sharing, you are literally making history and alleviating part of their pain
Please do not rely on me alone for sharing your campaign. I’m only 1 person and sometimes I’m not online which is unreliable. I never ignore anybody on purpose but I have a very limited capacity & very little energy and time.
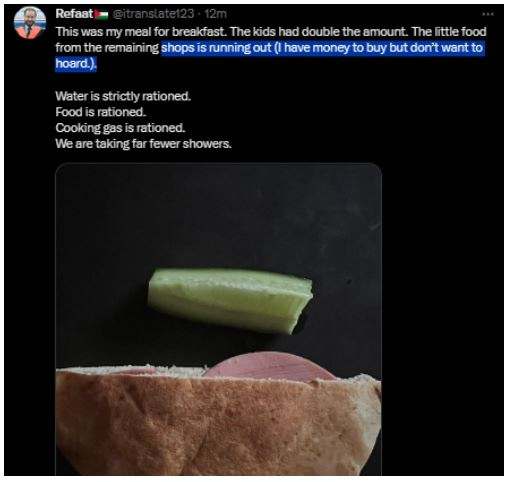
[Refaat Rafiq Alareer IF I MUST DIE] Refaat Rafiq Alareer was extremely hungry, November 2023, days before Refaat killed by Israel airstrike. If November 2023 already [one-by-one Gazan] extremely famine, extremely hungry, imagine November 2025 or more than 2 years Israel’s Genocide in Gaza.
[RENEW] 455 Languages IF I MUST DIE of Refaat Rafiq Alareer [by 6100+ Translators, Social Media Users]
Dec 9th, 2023, New York City, 4.10am —- with update total languages to be 310 as of July 1st, 2024, 3.52am New York City, and then, to be 350 languages as of July 28th, 2024, 1.37am ====== newest update as of July, 3rd, 2025 already 384 languages, and October 8th, 2025 reaches 455 languages across the globe.
Thanks for reading Prada’s Newsletter.















![[RENEW] 455 Languages IF I MUST DIE of Refaat Rafiq Alareer [by 6100+ Translators, Social Media Users]](https://substackcdn.com/image/fetch/$s_!jwSl!,w_1300,h_650,c_fill,f_auto,q_auto:good,fl_progressive:steep,g_auto/https%3A%2F%2Fsubstack-post-media.s3.amazonaws.com%2Fpublic%2Fimages%2Fc25bd266-d4e2-4169-a5e4-e901227a8b0c_725x560.png)


Solid breakdown on the contractor model for amphibious ops. The point about freeing up C-130s for more critical payloads really nails the efficiency argument here, especialy when we're talking about delivering small parts or medical supplies to isolated islands. Back when I worked on logistics projcts, the bottleneck was always having too few assets and too many low-priority runs eating up capacity. Contractorizing this niche makes sense for testing, but dunno if three years is enough to really stress test the model in a near-peer scenario.